At the turn of the 20th century, the Herero people, one the many Bantu tribes living in southwest Africa, watched as their territory was slowly swallowed up, shrinking the borders of their homeland. The loss of land was one of many objections they had to the German colonial rulers who had entered their territory and threatened their pastoral way of life. In an attempt to salvage the situation, they staged a secret uprising, attacking military posts and farms. They focused their attacks only on those with whom they had just grievances in the conflict -- avoiding women, children, German missionaries, colonists of different nationalities and rival tribes -- hoping to garner allies among others in the region.

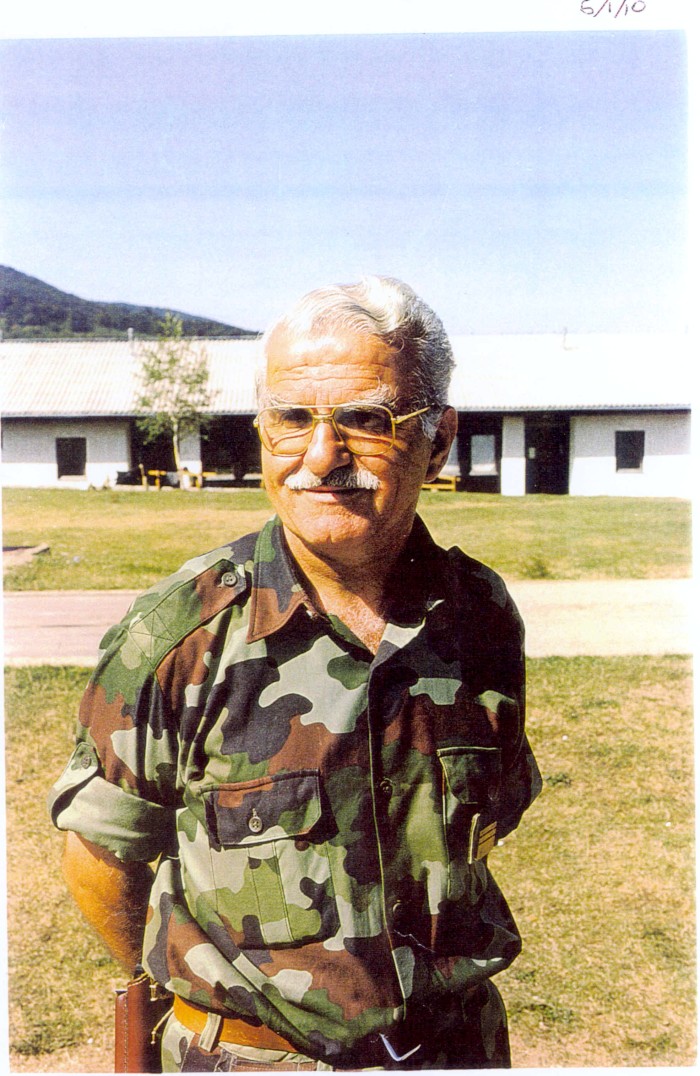
Lothar Von Trotha
The uprising began on Jan. 12, 1904. Farms were destroyed, forts were harried and some civilians were killed. What little the Hereros accomplished for themselves, however, would be extremely short lived. A new commanding officer charged with leading the colony's military forces; Gen. Lothar von Trotha -- soon set foot in the territory. His presence spelled doom for Hereroland.

African prisoners chained up by German soldiers, 1904.
With the use of 1625 modern rifles, 14 machine guns and 30 artillery pieces, The Battle of Waterberg took place in 1904, lasting two days. However, the outcome of the actual combat was less important than von Trotha's strategy of troop deployment, because the Hereros were boxed in. Hendrik Witbooi, the Nama leader, proved an exceptionally able guerrilla captain, and he inflicted a series of humiliating reverses on German troops. But his fighters had no answer to artillery, particularly as it was used against their women and children. So, like the Herero, the Nama were forced to sign a treaty placing themselves under German "protection". Three enemy sides were strongly defended, the fourth less so. As it became obvious the battle was lost, the surviving Hereros were forced to break free by way of the weaker path, the path which led into the brutal Omaheke Desert. Von Trotha pursued, ordering his troops to kill any who tried to flee the forced march or fell behind the main body in exhaustion. Once his quarry was trapped in the desert, von Trotha had his troops deny the Hereros access to water holes; later, he had those water holes poisoned. Hand-dug holes dozens of feet deep were later found in the desert wastes; desperate attempts to find water in the bleak landscape.

Von Trotha's stated goal was complete expulsion or annihilation. He had the edge of the desert fortified to keep the Hereros cordoned in the barren land. Throughout the ordeal, no prisoners were taken; young or old, healthy or infirm, weak or wounded, male or female. All were killed (or simply left to die) if encountered by patrolling soldiers. Sometimes, after what the Herero suffered at the hands of their captors, death was probably an escape. Eyewitness accounts preserve the horrors of the massacring.

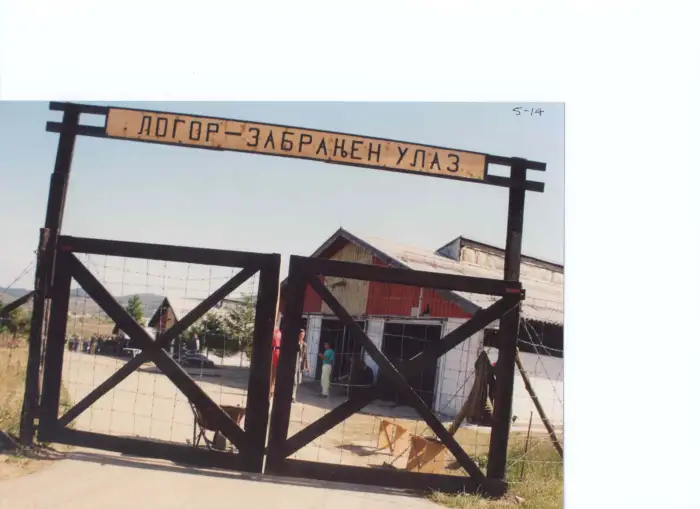
 Prisoners in a Labor camp
Prisoners in a Labor campThe Nama suffered at the hands of the colonists too. After the defeat of the Herero the Nama also rebelled, but von Trotha and his troops quickly routed them. On April 22 1905 Lothar von Trotha sent his clear message to the Nama: they should surrender. ‘The Nama who chooses not to surrender and lets himself be seen in the German area will be shot, until all are exterminated. Those who, at the start of the rebellion, committed murder against whites or have commanded that whites be murdered have, by law, forfeited their lives. As for the few not defeated, it will fare with them as it fared with the Herero, who in their blindness also believed that they could make successful war against the powerful German Emperor and the great German people. I ask you, where are the Herero today?’ During the Nama uprising, half the tribe (over 10,000) were killed; the 9,000 or so left were confined in concentration camps.

Prisoners bound by the neck to prevent escape
Forced labor inconcentration camps followed for those who survived the initial genocidal efforts. The death rates in the camps were staggering. Von Trotha was not completely successful, however. Some Hereros survived his horrific campaign, but their tribe's numbers were decimated. Estimates put the magnitude of the event into perspective. Out of an original 80,000 Herero people, only about 20,000 escaped von Trotha's death crusade alive; that's three quarters of the entire population, completly wiped from existence.
In the Herero work camps there were numerous children born to these abused women, and a man called Eugen Fischer, who was interested in genetics, came to the camps to study them; he carried out medical experiments on them as well. He decided that each mixed-race child was physically and mentally inferior to its German father

Soldiers began to trade in the skulls of dead Herero and Nama people.
It is estimated that up to 2000 pastoralist Herero escaped eastward in small numbers into the Kalahari desert, into what was then the British protectorate of Bechuanaland (Botswana). Included was Samuel Maharero, the Herero leader. His people arrived with little or no cattle and became subservient to the Tswana - Bechwana chieftain of Sekgathôlê a Letsholathêbê.
The Nama led by Hendrick Witbooi, had fought with the Germans against the Herero. Regardless, von Trotha turned his murderous attention to him, sending Witbooi, Cornelius Fredericks and other chiefs the following message; The Nama who choose not to surrender and lets himself be seen in the German area will be shot until all are exterminated. Those who at the start of the rebellion committed murder against whites, or have commanded that whites be murdered have by law, forfeited their lives.
Hendrik Witbooi was killed. In September 1906, Cornelius Fredericks and the fighters of Witbooi surrendered and were sent to Shark Island. Death in the camp was meticulously recorded. Solders were tasked with naming the dead and recording numbers. Their records show that of the 1795 Nama prisoners who had arrived, only 763 were alive in April. One thousand thirty two had died. The detailed record shows that of the living, 123 were in such poor health they would soon die. By 1908 when the camps were closed, disease and malnutrition had killed up to 80% of all prisoners who had entered Shark Island - including Namaqua chief Cornelius Fredericks.

Shark Island
Prisoners were intentionally placed on the exposed northwest point of the barren island - infamous for its bitter cold arctic gale force wind. Diseases in the camp were rampant and intentionally left out of control. The unhygienic living quarters, lack of clothing and high concentration of people contributed to disease which rapidly spread. (typhoid) Huddled together and suffering from malnutrition, the prisoners began to die. Statistics show that as many as 80 % of the prisoners sent to this concentration camp never left the island alive.